Clean it up \ performance issues
Performance issues? First, is it the computer or only the Internet that seems slow? If just the Internet, see our HiJacked? and Internet Speed articles.
But if the computer is slow in general, e.g., starting up, opening a local application, game, etc., try some of these, especially checking for disk errors...
As with all of our suggestions, you apply
these at your own risk.
And as always,
BACKUP, BACKUP, BACKUP!
We will refer to the Run Command, Command
Prompt and Administrative Command Prompt.
If you are not sure how to get there, see
command.
From time to time it is a good idea to clean up your machine, but that does not mean going through and haphazardly deleting files or folders!
Drive activity light
Most computers have a drive activity light (small LED that flashes with disk activity). It's a quick indicator as to the current state of your computer. A nearly solid drive light is indicating the drive is busy doing something, but it may be indicating a failing hard drive. See Checking for disk errors below.
You may also want to run the manufacturer's drive diagnostic/tests to see if the drive itself is failing. Most manufacturers have built-in diagnostics but getting to it can be a bit challenging. With the computer shut off, start the computer and immediately start pressing the key necessary to enter the diagnostics mode.
There is no consistency between manufacturers and for that matter, from a given manufacturer. Seems like all of them have used different utility keys over the years. Escape and F12 are the popular keys. But be careful, you DO NOT want to enter the BIOS setup or Factory Restore/reset modes. If you can't get there, try searching support for diagnostics at the manufacturer's support site.
Odd performance issues
Using the Task Manager (Ctrl+Alt+Del), check for excessive CPU usage by the various processes.
Windows 7 (Windows 10 below): Other than Idle process, if you have something using more than a few percentage of the processor (CPU), do some research on it.
![]()
In the Task Manager
sort by CPU usage by clicking the CPU column header.
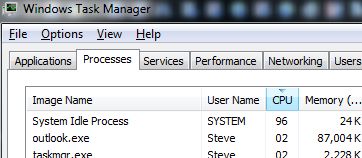
Windows 10 does not show system idle rather it shows nothing at
all so in Win10, look at the total CPU usage and if more than a few
percent, start researching.
From Microsoft, there are a bunch of system tools available. Of interest in performance issues may be Processes Explorer which breaks down the CPU usage further than the Task Manager shows.
See also our Autoruns, Processes, Locked up computer and Windows 10 update articles.
Note: We have seen where McAfee is in process of system scan while you are using the computer. It should be scanning only when the computer is idle and it should detect you are using the computer then pause the scan, but it does not always do so. Worse of all, that surprise scan cannot be canceled! Nice move McAfee...
Unnecessary programs
Begin by looking in the Control Panel's Programs and Features. Look through the list and if you find applications, games, etc., you no longer use, select that item and then click the Remove/Uninstall button.
But be sure to remove only what you no longer use. If you find items listed you are unsure of, search the Internet for that item and see what it is. Your option, but unless you specifically use them, we recommend uninstalling all Internet Explorer toolbars.
Also see brute uninstaller information here.
Crap/Junkware, Toolbars and Hijacking
See Hijacked!
Temporary files (Internet and others)
The Internet browsers all store "temporary" files on your computer to help speed things along, e.g., all those images, icons, logos and so on. By storing them on your computer instead of downloading them each time you visit a site, the Internet will be a bit quicker.
It is after all a computer and sometimes for no reason at all, files become corrupt! Corrupt temporary files can cause slow web pages, empty/blank web pages and even browser crashes, so clean them up. See our Cookies page.
But those are not the only temporary files, in fact, there are lots of them. If the computer is running slow (not just the Internet), the Windows system temp folder can be safely emptied as a start to your diagnostics.
From the Run command, type %temp% then press Enter.
That opens the Windows temporary files folder. Press CTRL A to select all files. Hold the Shift key then press the Delete key. Notes:
- There will be some files you cannot delete as they're in use. You could delete those as well if you restart in the safe mode but probably not worth that effort.
- You may be prompted the folder will no longer be "shared" - YES, delete those too. There shouldn't be any shared folders in the temp folder.
- You may get a prompt you need higher permissions level to delete - CONTINUE, that stuff can go as well.
We have seen just a couple machines so far where the temp folder is full of folders, typically just a 3 or 4 character name, but hundreds of them. You delete all and they come right back after booting. We may have stumbled on some scheduled tasks causing this problem. Try deleting (or at least disabling) any computer and printer manufacturer tasks, but from there the only solution seems to be reinstall Windows from scratch.
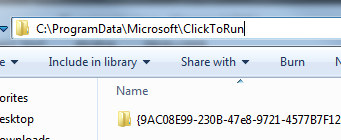
Microsoft Office may build hundreds of temporary folders and log files, and these can add up to 1/2 or more of the available disk. There are two potential places these temp files may build: C:\Windows\Temp and C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\ClickToRun
Everything in the C:\Windows\Temp folder can be deleted. Use Shift Delete so they don’t just go to the recycle bin. Note: Some may be in use so just “skip all” of those.
|
The C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\ClickToRun is a hidden folder but typing that location in the File Explorer's addressbar should get you there. Sort this list by date modified and (shift) delete old
stuff. |
 |
We have not found a real good way to prevent these temporary Office files so as you notice the disk filling, repeat the processes…
Cleanup manager
From the Run command type cleanmgr then press Enter. If prompted, the drive of interest is "C:" and select the various cleanup options as desired...
Windows Vista/7/8/10 may offer to
cleanup all files on the computer, select that option.
When the cleanup manager opens, place a check mark in every
option (except compress old files Windows XP - as that may actually slow the
computer performance). Recycle folder is optional! We
never empty ours...
Check for disk errors
It's a good idea to check the disk for errors, if the computer:
- had a sudden shut down due to a power outage or the like.
- was shocked, e.g., kicked, fell over or abruptly moved while it was on (laptop owners take note of that!).
- running unusually slow, but after you have eliminated the possibility of a virus or software issue.
There are reports of disk corruption if chkdsk is ran on a Solid State Drive (SSD) so best you do not!
Be aware, this
check could take a couple of
hours.
Under Windows 10, it will seem to hang at 10-20 percent.
Don't panic and especially, don't shut it off!
Must be at an Administrative prompt type chkdsk /r (then enter)
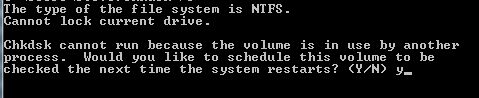
Answer the prompt with a Y then press enter. Reboot the computer for the scan to begin.
Chkdsk notes:
- There is a space between chkdsk and the slash, but not between the slash and the r.
- If bad clusters are found, it could be an indication the drive is failing, but a couple bad clusters are not uncommon.
- If the process gets "stuck" be patient but if an hour goes by at the same percentage/cluster count or file count, you have a hard drive problem.
-
If the utility reports the disk is "raw"
and/or it will not execute,
try reissuing the command and rebooting.
If it fails a second time, there may be a bigger problem...
The manufacturer's also include a disk test utility...
You can typically get to it by tapping Esc or F12 immediately after a cold start. But there are no standard out there so if Esc or F12 don't offer diagnostics, search support at the actual manufacturer's support site.
Defrag
Start > Search "defrag"
![]() This too will take some time...
This too will take some time...
But with very fast CPUs and hard drives, this is simply not as necessary these days.
- Never defrag a solid state drive (SSD).
SFC Scan
Run this if you are having odd problems with Windows. From the run command type sfc /scannow then press Enter. SFC Notes:
- To run, use an Administrative prompt
- If problems are found, you may be prompted for a Microsoft Windows CD. Some manufacturers System Restore CD's like HP/Compaq, Sony and others will not work as they are part of a restore kit, they are not the needed Microsoft Windows OS disk. Do NOT run those CD's as they may restore to factory condition and you will lose everything.
Change Dropbox settings
Change the bandwidth settings to limited. 50k download and 50k upload:
In Window's system tray, right click Dropbox, click the "gear" then select preferences. In that window you will see the bandwidth options...
Turn off indexing
|
Another issue we see on occasion is the Windows Indexing is a bit to aggressive. More so on under Windows XP but possibly 7 and later. While it makes for quicker local searches, the indexing could very well slow the computer a lot and our recommendation is to simply turn it off. Windows 7 and later: Control Panel > Programs and Features > Windows Features and uncheck Indexing Service. |
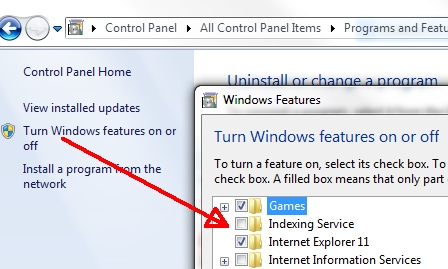 |
Windows 10 (last resort)
Try: Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
at an
Administrative prompt
See: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh824869.aspx