DNS
Domain Name System (or Service) is how the Internet can properly route your request for a website. The link explains DNS completely but briefly: www.microsoft.com is actually an IP address (a set of numbers). So when you type www.microsoft.com in the addressbar, your request is first intercepted by a DNS server. The DNS server looks up the IP address of your request then forwards you to the desired website.
Hijacked DNS settings
We have seen where computer's DNS setting were hijacked, so instead of obtaining the DNS addresses from the router or your provider, there were hijacked DNS settings (see below). Those hijacked DNS settings meant everything done on the Internet was FIRST routed through that hijacker's server, so they were seeing (maybe even recording) everything you do.
If you are getting redirected, i.e., want to go to one website but end up at another site, or you suddenly have all kinds of ads popping up, or get a lot of page not found (404) errors or have any other strange issues with the Internet, get your computer checked! See Hijacked! for more.
DNS issues...
By default, the DNS addresses used by your router and browser are assigned by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and automatically obtained. But like any other computer, DNS servers can go down (typically it's only for a moment). Sometimes DNS servers are removed from service then replaced with different DNS servers. If the DNS servers change (and you will never know when they do), generally powering off and up your modem and router will pickup those changes.
Check the current DNS assignment in the network status. Windows 7 or 10 you can right click the network icon in the taskbar by the clock or get there via the Start menu...
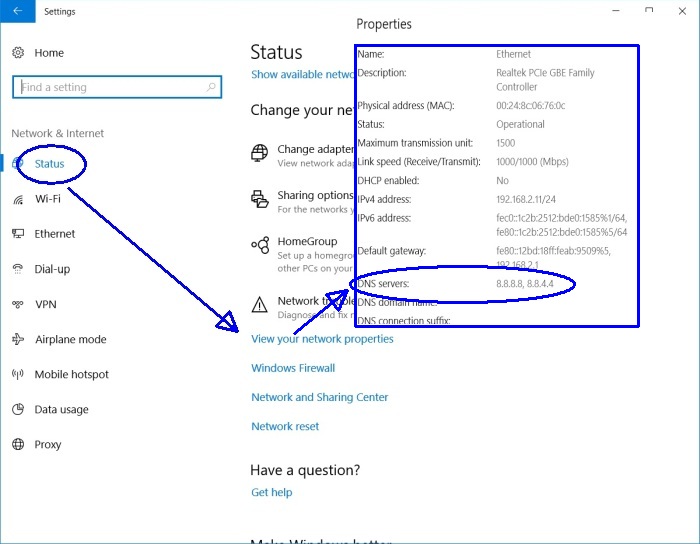
Windows 10
Start menu > Settings > Network/Internet > Status (left) > View properties (lower center). That opens a new window showing the current settings. (We've overlaid that new window over the Status window).
Windows 7
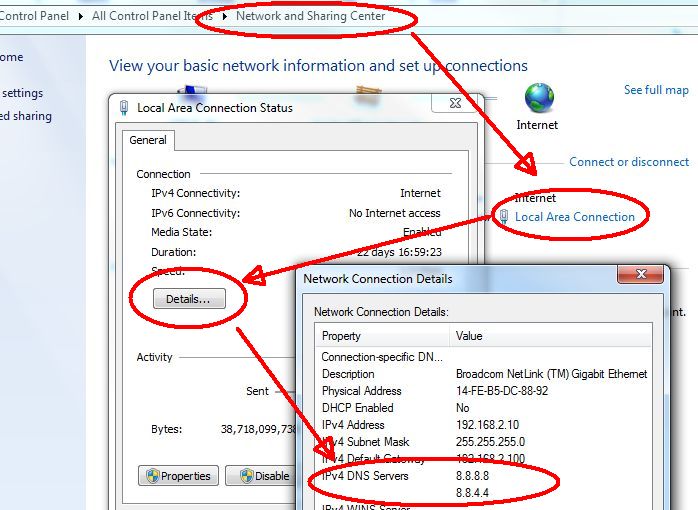
You may find the DNS server has only one address and it is the same as the gateway. This means the router (via your ISP) is acting as the DNS server(s).
If you find your provider is continually having DNS issues...
you may consider using Google's DNS addresses of: 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 instead.
- See our May '18 newsletter for another option of 1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1
If you have a router, that is where this change should be done. See Routers
If your computer connects directly to the DSL modem, you can over-ride the ISP assigned DNS addresses in the network connection properties...
|
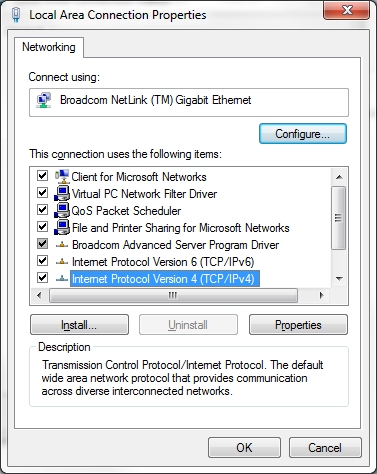
1) Windows Vista, 7, 8 and latter - open the Network and Sharing Center, click on the Local Area Connection (or "Wireless" when applied). 2) Click the Properties button (not shown). |
 |
|
3) Then from the list, locate
and select Internet Protocol TCP/IP Version 4 and click
Properties.
|
4) Leave the top section as is, changing only the lower DNS
server information. 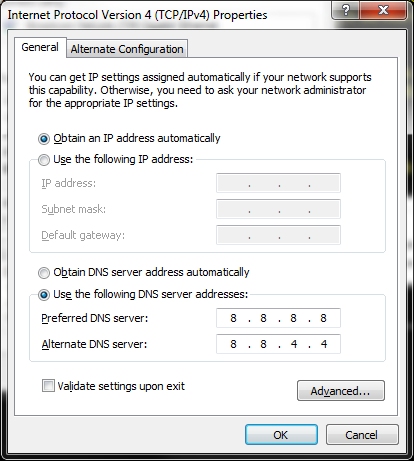 |
Note: If you want to, you could have the ISP DNS addresses under Advanced for a total of 4 DNS servers, but that's really not necessary.